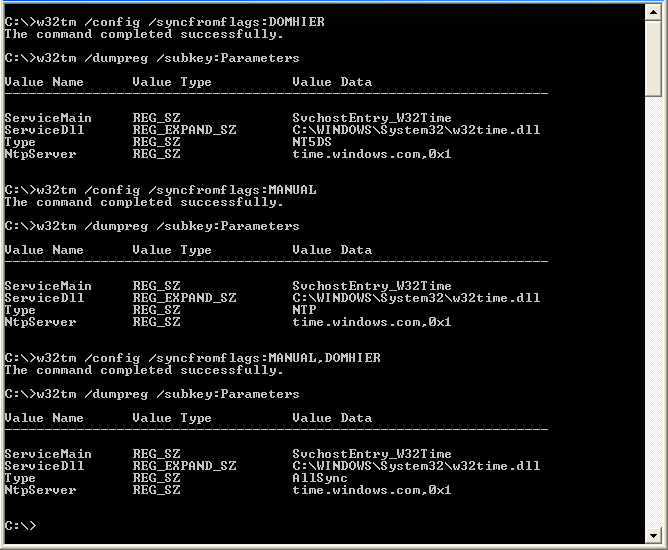
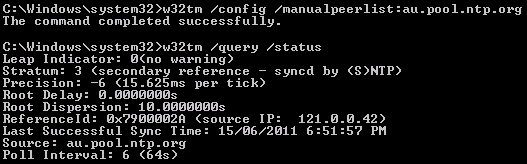
The output of your w32tm /query /configuration shows that the Windows Time service settings are being managed by Group Policy You need to make your desired changes in the GPO that's being used to configure the Windows Time service – joeqwerty Nov 9 '19 at 235 2 show ntp status This is an example of output from the show ntp status command USSP3SSW01#sho ntp status Clock is synchronized, stratum 2, reference is nominal freq is Hz, actual freq is Hz, precision is 2**18 reference time is DF ( UTC Fri ) To set the time ( Tested against Windows 16) Launch CMD as administrator exampled c\time AM – This will set the time to 9am Note a time source if domain joined will up date the time clock again Check the source c\w32tm /query /status Will show the time "Source" To set an internet based NTP

How Can I Check A System S Current Ntp Configuration Super User
W32tm /query /status output explained
W32tm /query /status output explained- You can use the W32tmexe tool to configure Windows Time service (W32time) settings You can also use W32tmexe to diagnose problems with the time service W32tmexe is the preferred commandline tool for configuring, monitoring, or troubleshooting the Windows Time service For examples of how you can use this command, see Examples SyntaxThe option /ntpte will output three timestamps The first hex number is an NTTE date (as also understood by w32tmexe /ntte), followed by the ANSI date (number of days since 1st Jan 1601) followed by the date/time in readable/local format




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense
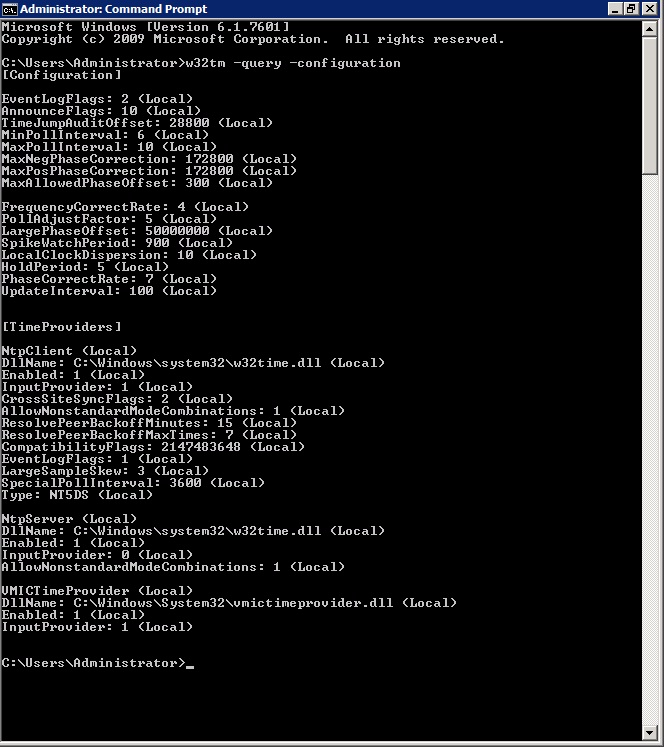
If I edit the regkeys manually, to change the NTP server hostname from timewindowscom to something else, then run w32tm /query /configuration, the output from that query still shows the previous value If I stop and then start the w32time service, and then issue the query again, it now reflects the adjusted settingsCreated 2 scripts, one that will check which time source is being used, and one that measures the time difference But now it want to combine those script and i'm not sure how to do it w32tm once W32tm performs numerous commands Their results are displayed on the screen net start w32time ;
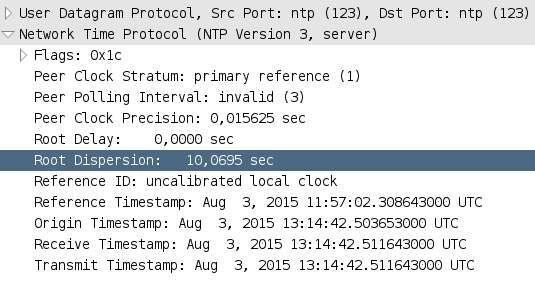
I have recently been configuring time sync for a new DC on an existing domain (to replace an old DC holding the FSMO roles and set as the reliable time source) On one member server I saw a Root Dispersion of about 4 seconds when running w32tm /query /status which concerns me slightly, so I want to find out what it means› w32tm query status explained If I edit the regkeys manually, to change the NTP server hostname from timewindowscom to something else, then run w32tm /query /configuration, the output from that query still shows the previous value If I stop and then start the w32time service, and then issue the query again, it now reflects the Run the following and post the output to a message, not an attached file w32tm /query /configuration w32tm /query /status Time /T If you wish to set your system up for a higher time accuracy, see the following Configuring Systems for High Accuracy Microsoft Docs
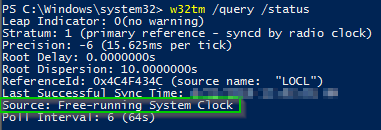
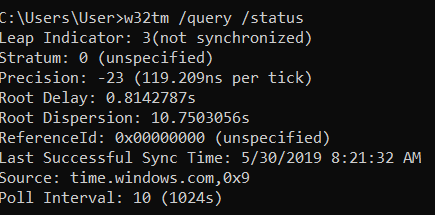
Still seems to be fairly close, it no longer says local CMOS clock when I do w32tm /query /status C\Windows\system32>w32tm /query /status Leap Indicator 0(no warning) Stratum 1 (primary reference syncd by radio clock) Precision 6 (ms per tick) Root Delay s Root Dispersion s ReferenceId 0x4C4F434C (source name So according to the output, the type is correctly shown as NTP and not Nt5Ds I then run a sync >w32tm /resync Sending resync command to local computer The computer did not resync because no time data was available Ok so we have an issue I check the peers list >w32tm /query /peers#Peers 1 Peer State Pending Time Remaining sLinux How to determine NTP communication status › On roundup of the best images on wwwstackoverflowcom Images Posted (5 days ago) I looked at ntpwait's source (it's Perl), and it is just parsing the output of ntpq c "rv 0 state", but it isn't doing a good job of it (eg the current output of that ntpq command is ***A request variable unknown to the server,



Pdc Correct Time Settings More In Depth Using W32tm Sikich Llp



Check Windows Time Settings Mcb Systems
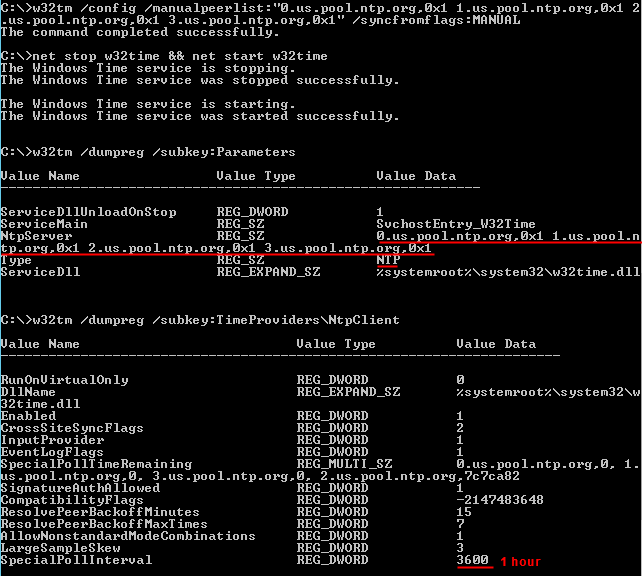
W32tm /query /peers w32tm /query /status w32tm /query /configuration w32tm /query /source I configured the PDC to sync to external sources and made sure it was set to be a reliable source Example NTP peer list for a PDC How to run w32tm in nonelevated powershell I am writing a helper script that will go through a list of servers and verify they are in sync with the NTP The script shall be run as a normal script on request by the facility operator and shall request for Admin credentials if the target is not in sync We unfortunately cannot change the NTPW32tm /query /peers The output of this command also shows a mode for each specified server/peer, which should be 3 (Client) in most cases For other options of the w32tm command please see the usage information displayed if the command is run without any parameter



Basic Windows Time Service Setup Mcb Systems



Managing Windows Time Service Ntp
My task is to get the current time with the w32time service from a Windows 16 Server, and compare it to the time showed on this server What I find online about this service is synchronising, and doing more complicated stuff, but I simply need the "official" time in the simplest form, so I can compare the two, and check if there is more than a few seconds ofPosted (6 days ago) Once the NTP synchronization has started you can query the status with the command ntpq p as in the image below Reachvalue explained The value in the reachcolumn represents the success and failure of the past eight polls to the NTPserver It is a bitshift register, which means that bits are added to w32tm /query /status You can also see what peers (sources) it is set for by using the command w32tm /query /peers In this instance, its source is "Freerunning System Clock" If it is in this state or "Local CMOS clock" and the machine exists as a virtual machine on VMware ESXi or Microsoft HyperV then it may be temporary




Validation Guide Rs5 High Accuracy Time




How Can I Check A System S Current Ntp Configuration Super User
Check Ntp Status Linux University Education 5 hours ago Checking NTP Status NTPEducation Just Now You can verify that NTP operation and status from any router on the network The show ntp associations command output is the same as that of the FreeBSD ntpqp utility The first column in the output, remote , shows the servers and peers that you have configured on the router, SysAdmin Horror Stories Vol3 – FREE eBook anyweb posted a topic in Official Forum Supporters The previously published SysAdmin Horror Stories Vol1 and Vol2 highlighted some of SysAdmins' funniest and most horrifying stories They proved so successful, that Altaro decided to produce a third and final edition they've› w32tm query status explained How do I interpret w32tm output?




Configuring Active Directory Time Using The W32tm Utility Chinny Chukwudozie Cloud Solutions




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros
The default value is 3 The allowed range is 1 through 50 w32tm /ntte Converts a Windows NT system time, in (10^7)s intervals from 0h 1Jan 1601, into a readable format w32tm /ntpte Converts a Network Time Protocol (NTP) time, in (2^32)s intervals from 0h 1Jan 1900, into a readable format w32tm /resyncType net time /querysntp, or;When there is a problem, the configured (S)NTP server can be tested by issuing the "w32tm /stripchart / computerdepoolntporg", which should result in the output displayed in the figure below Figure test the (S)NTP service When an unexpected result is returned, it is recommended to check access to the specific (S)NTP server A firewall




Windows Time Service Tools And Settings Microsoft Docs



Time Synchronisation Electric Monk
Check it with W32tm /query /configuration You may have to repeatedly run it a few times until you see it change from If you want to know what your domain controllers Time Server configuration is you can run two simple command line query's Open a CMD prompt;Type w32tm /query /status;




Fast Troubleshooting For Windows Time Service W32time Synchronization
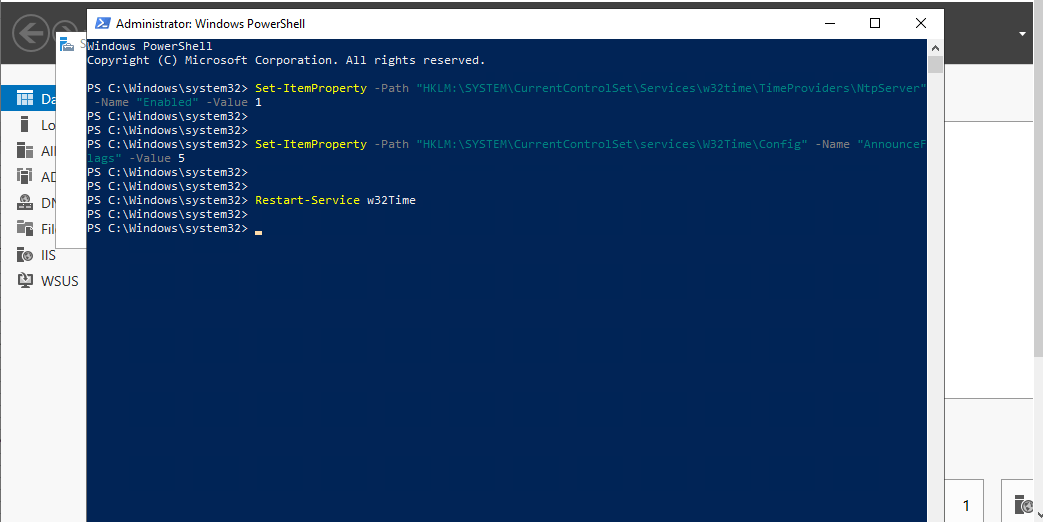



Windows 19 Archives Foldersecurityviewer Blog
W32tm Local CMOS Clock VMware Open a command prompt Check time sync w32tm /query /source If the output says Freerunning System Clock or Local CMOS Clock, the server is not using NTP List NTP server list w32tm /query /peers If the output shows that the peer list is empty and state pending, the server is not using NTP Polling Intervals and Clock Corrections Explained SpecialPollInterval This value, expressed in seconds, controls how often a manually configured time source is polled when the time source is configured to use a special polling interval If the SpecialInterval flag is enabled on the NTPServer setting, the client uses the value that is set as W2K8R2 w32tm /query /source returns Local CMOS Clock Recently I was working on a windows 08 Domain controller, where everything was looking fine even the DCdiag was clean There were some intermittent DNS not working issues reported for which I was digging around Thats when I saw that the clock was off by 3 mins or so, though that shouldn
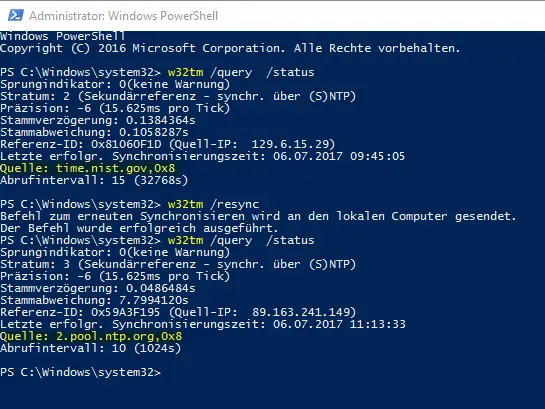



How To Configure Ntp Server On Windows Server 16




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros
Check time sync w32tm /query /source If the output says Freerunning System Clock or Local CMOS Clock, the server is not using NTP List NTP server list w32tm /query /peers If the output shows that the peer list is empty and state pending, the server is not using NTP Update the peer list › Course Detail wwwvmwarecom Show All Course Then I start the W32Time (Windows Time) service because the w32tm command requires it As you can see, all parts of the code that can possibly generate an exception are enclosed in Try / Catch block because I do not want to stop the execution of the script, and I want to have information about any exception in the ErrorEvents property of theI have followed the instructions presented at the site below and everything seems to be working just fine Yet when I run the command "w32tm /query /peers /verbose" on some servers for some peers I will have output like this All of these servers are on a local network on the same subnet All firewalls are disabled, DNS forward and reverse
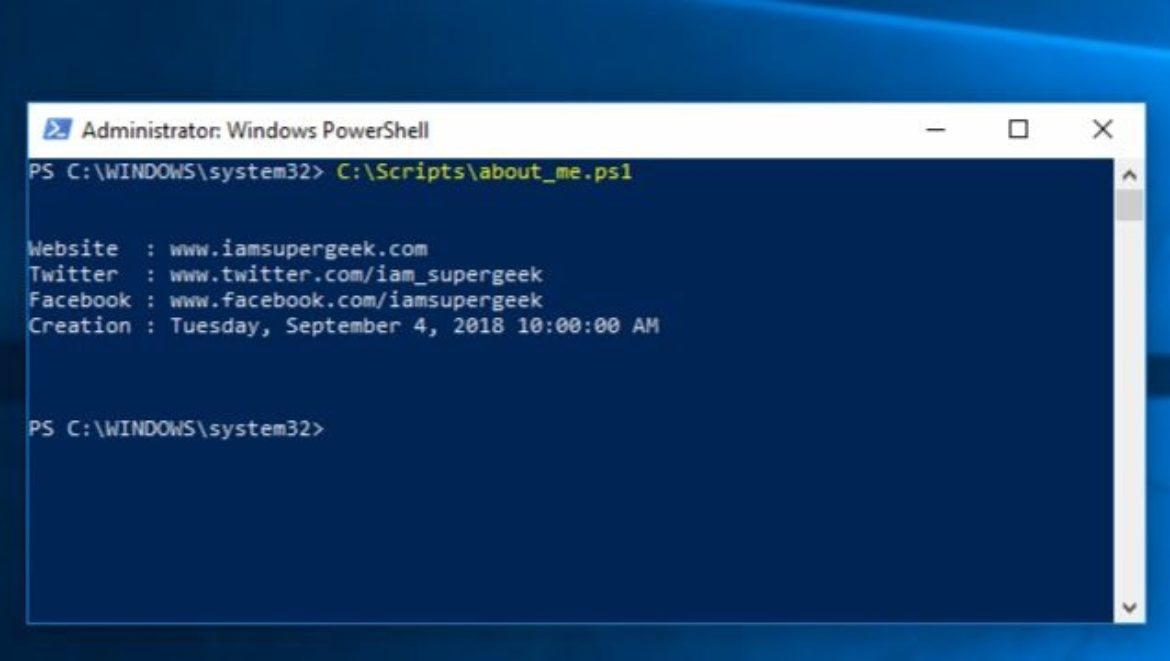



How To Fix Time Drift For Off Prem Domain Pcs Iamsupergeek




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense
The console application w32tmexe allows monitoring of the offset of the local time to the time of an internet time server The easiest way to do this is from aPowershell Time A Command University Education 8 hours ago Measure the runtime of a PowerShell command 4sysops Education 5 hours ago Mon, powershell, powershell beginner 4 Using the MeasureCommand cmdlet in PowerShell is an easy way to measure the runtime or execution time of a commandThis can also tell you how long a customProcedure Open a command prompt Check time sync w32tm /query /source Check if the server is now using NTP w32tm /query /source If the output shows one of the servers in your peer list, the server is now using NTP If the user uses a Windows Server as NTP server, the rootdisp may be higher than 1000




Configure Windows Server To Query An External Ntp Server




Window 10 As Ntp Server Ip On Wire
The w32tm /query /status command also shows the machine's time source, as well as other potentially useful information The /verbose switch provides even more information As with the first command, these switches are only available on machines running Windows Vista or later To see the SystemClockRate and pollIntervalInSeconds values (measured in seconds), open a Command Prompt window and then run W32tm /query /status /verbose This command produces output that resembles the following The output presents the poll interval in both clock ticks and in secondsBelow are the full details of the W32TM commandlet which has been the standard since Windows Vista and Windows Server 08 and still function in Server 12 R2




W32tm Query Status Malfunctioning Clock Time Work Up And Microsoft Community




Window 10 As Ntp Server Ip On Wire
The option /ntpte – will output three timestamps – The first hex number is an NTTE date (as also understood by w32tmexe /ntte ), followed by the ANSI date (number of days since 1st Jan 1601) followed by the date/time in readable/local format0808 ds os 0808 is local time ds is the internal delay (time difference between the udp package received and udp package sent on the server side os is actual offset between the
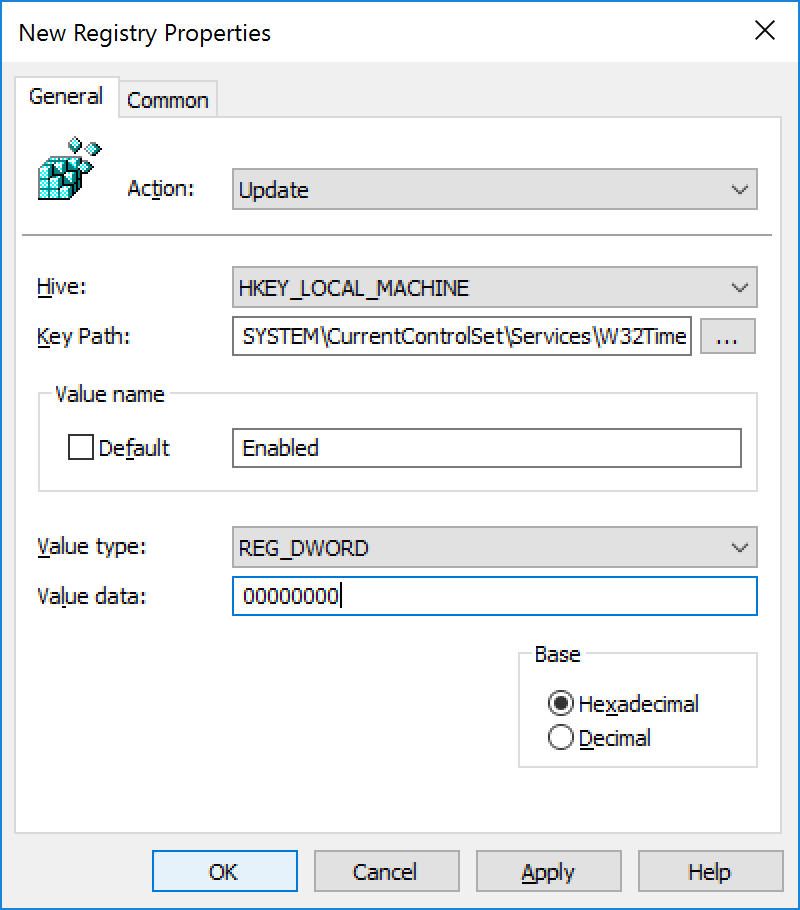



Active Directory Jack Stromberg




Domain Controller Time Won T Sync With Ntp Server Server Fault




Window 10 As Ntp Server Ip On Wire



How To Set And Change An Ntp Time Source In Windows Server 08 R2 Sbs 11 And Vanilla Server A Windows System Admin S Blog



W32time Archives Foldersecurityviewer Blog




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros



Ntp Server Configuration On Server 12r2 Not Working




How To Find Ntp Server In A Domain To Sync All Pcs



Psa Time Windows Com Ntp Server Seems To Be Sending Out Wrong Time Sysadmin



Pdc Correct Time Settings More In Depth Using W32tm Sikich Llp




How To Configure Time Services In A Bvms Version 10 1 Environment




Configuring Active Directory Time Using The W32tm Utility Chinny Chukwudozie Cloud Solutions




W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz




Ntp Configuration For Time Sync



Troubleshooting Ntp Sync To Windows Time Servers
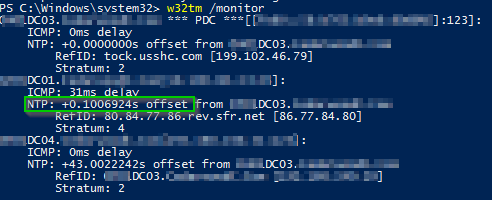



Pdc Correct Time Settings More In Depth Using W32tm Sikich Llp




Fast Troubleshooting For Windows Time Service W32time Synchronization
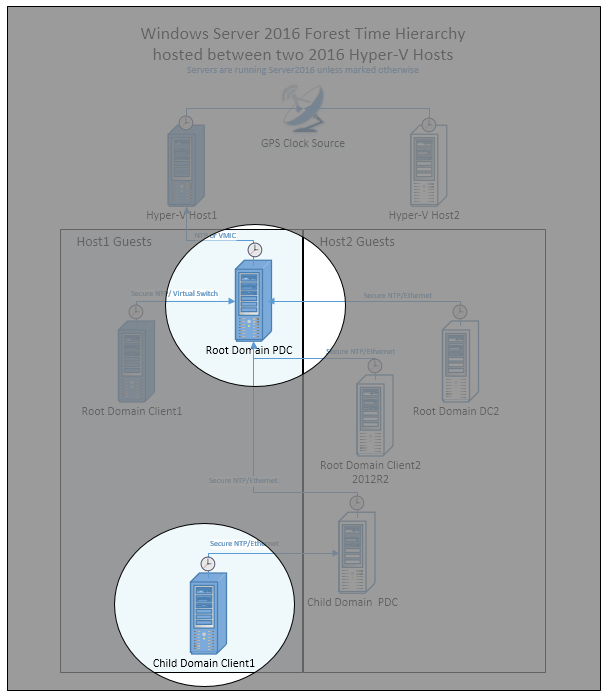



W32time Archives Foldersecurityviewer Blog




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense




Ntp Configuration For Time Sync




Fast Troubleshooting For Windows Time Service W32time Synchronization



How To Sync Time From External Time Source



2




Window 10 As Ntp Server Ip On Wire



Xenserver Tools Timesync Disable Page 3 Guest Runtime Discussions




Setting Up And Managing Ntp Active Directory Gpo



Pages About Contact Me Archives June 14 May 14 December 13 November 13 June 13 March 13 February 13 January 13 December 12 November 12 August 12 February 12 December 11 November 11 October 11




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros




W32tm Query Status Malfunctioning Clock Time Work Up And Microsoft Community
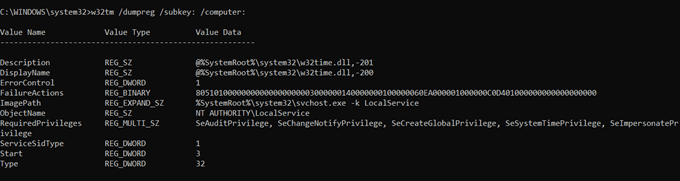



How To Find Ntp Server In A Domain To Sync All Pcs




W32tm Query Status Malfunctioning Clock Time Work Up And Microsoft Community



Sperrgebiet S World Time Synchronization With Virtual Domain Controllers
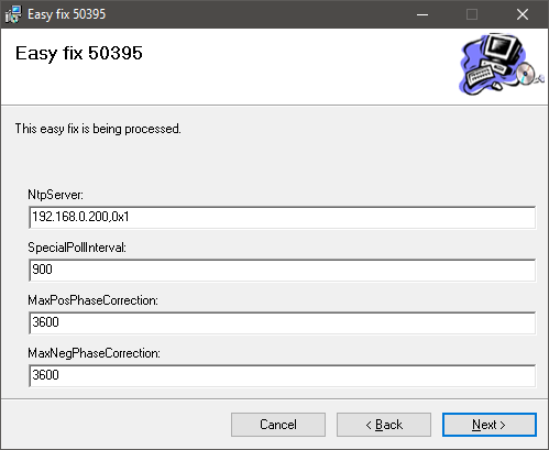



How To Configure Time Services In A Bvms Version 10 1 Environment
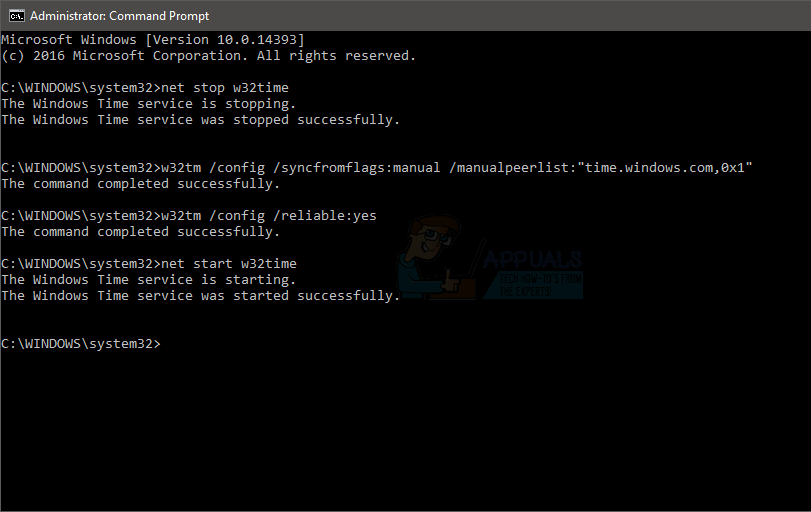



How To Configure Windows Server To Query An External Ntp Server Appuals Com



W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz




W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense




Solved Dc Not Respecting Time Servers Active Directory Gpo




Ntp Server Issue On Pdce Windows Server




W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz



Active Directory Time Synchronization Technet Articles United States English Technet Wiki
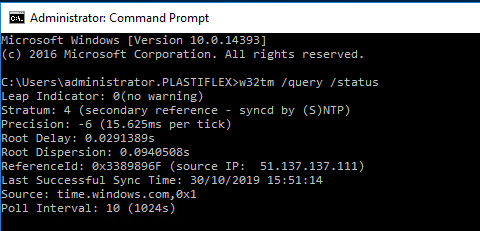



Windows Server 16 Sync Time Server Using S Ntp Audministrator
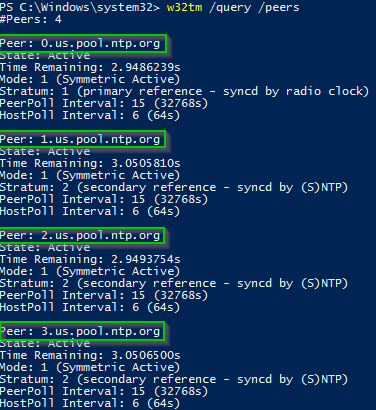



Pdc Correct Time Settings More In Depth Using W32tm Sikich Llp




Solved Dc Not Respecting Time Servers Active Directory Gpo




Install Archives How To Blog



Windows Ntp Server Windows Ntp Cookbook Icookservers Networks




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros



Time Problems W32tm Sync Isn T Perfect
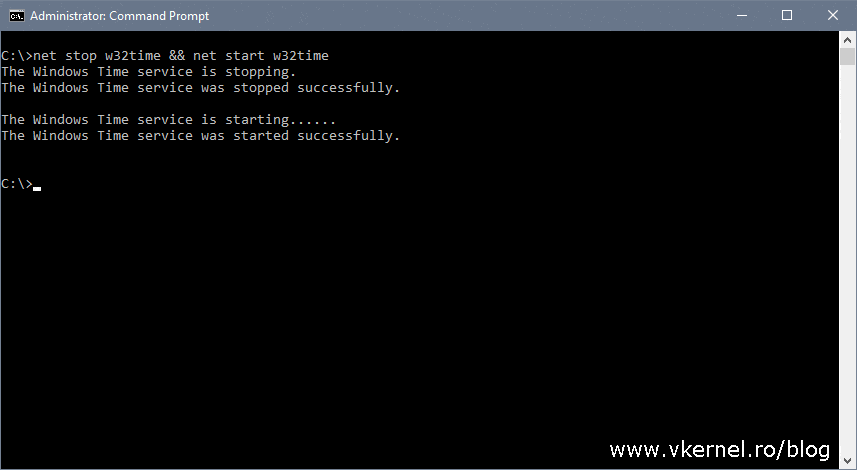



Configure Dc To Synchronize Time With External Ntp Server




W32tm Problems Can T Sync With Ntp Server Microsoft Q A




W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz



Network Time Polling Interval



Timesync




Ntp Server Issue On Pdce Windows Server




How To Create A Standalone Ntp Server With Windows Interface Technical Training



How To Find Ntp Server In A Domain To Sync All Pcs



Script To Create Group Policy Objects And Wmi Filters To Manage The Time Server Hierarchy J House Consulting Devops Microsoft Citrix Desktop Virtualisation Vdi Specialist 61 413 441 846



Just Another Windows Noob This Is A Blog By Niall C Brady Enterprise Mobility Mvp Page 5



W32tm Query Peers Verbose Lastsyncerror 0xfd The Trust Relationship Between This Workstation And T He Primary Domain Failed




Windows Time Service Tools And Settings Pdf Windows Registry Group Policy



Documentation That Explains The Output Of W32tm Command




How To Configure Time Services In A Bvms Version 10 1 Environment



Troubleshoot Ise And Ntp Server Synchronization Failures On Microsoft Windows Cisco




Configure Ntp Time Sync Using Group Policy Theitbros




Ntp Configuration For Time Sync




How To Create A Standalone Ntp Server With Windows Interface Technical Training




W32tm Query Status Pending W32tm Query Status Pending Blogjpmbahe0amz




Time Configuration For A Virtualized Domain Controllers Theitbros




Fast Troubleshooting For Windows Time Service W32time Synchronization




Ntp Configuration For Time Sync



Verify Your Windows Time Service Networknet Nl




What Is Windows S Time Server Synchronisation Precision And Does It Compensate The Ping Time Super User



Active Directory Time Synchronization Technet Articles United States English Technet Wiki
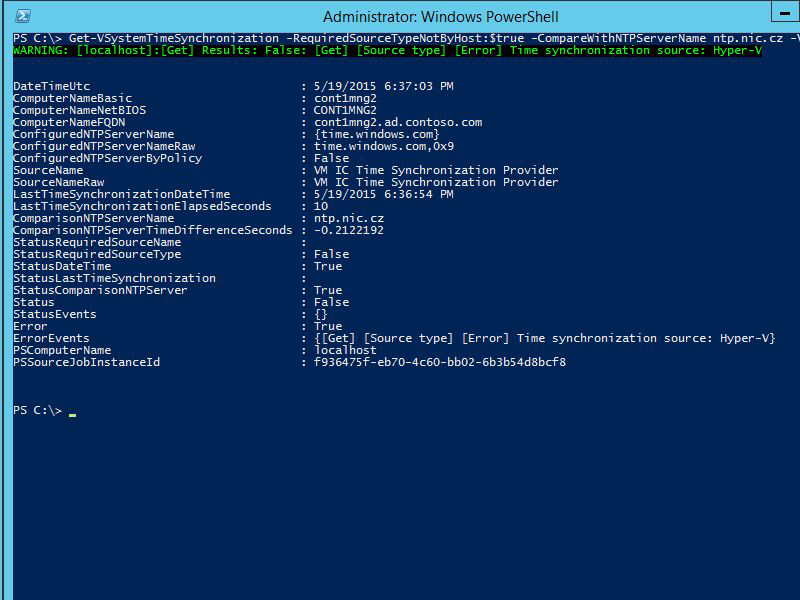



Powershell Time Sync Get And Evaluate Synchronization State Scripting Blog




Configure Windows Time For The Domain Marc Kean




Domain Controller Ad Time Is 9 10 Minutes Fast Server Fault



Ntp Server Configuration On Server 12r2 Not Working



W32tm Query Peers Verbose Lastsyncerror 0xfd The Trust Relationship Between This Workstation And T He Primary Domain Failed




Check Ntp Server Working Or Not Check Ntp Server Date And Time Windows Linux Blog D Without Nonsense


